Altmetric Score
Dimensions
Citation
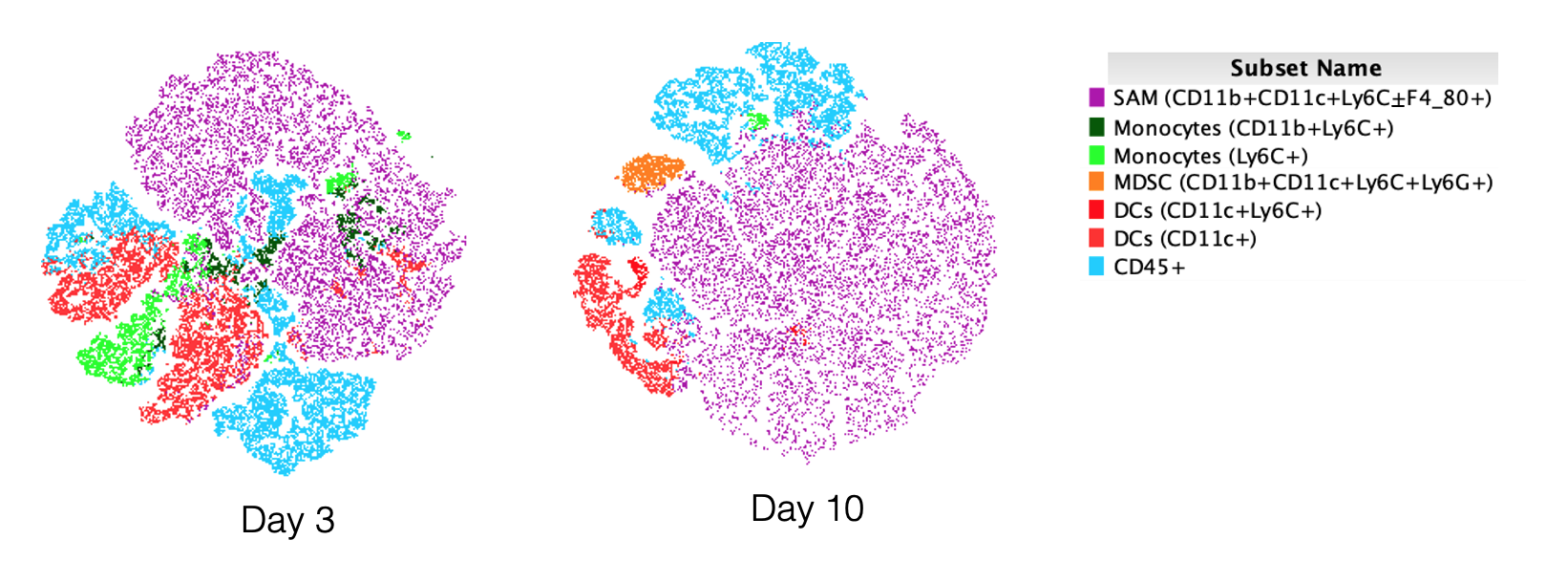
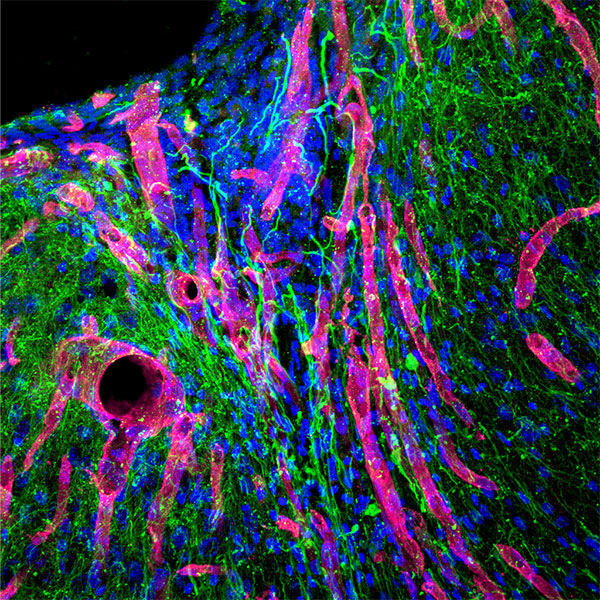
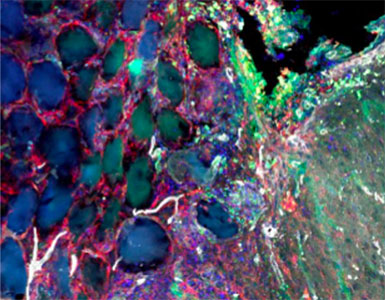
Study designA controlled, interventional animal study.ObjectiveSpinal implant infection (SII) is a devastating complication. The objective of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of a novel implant coating that has both a passive antibiotic elution and an active-release mechanism triggered in the presence of bacteria, using an in vivo mouse model of SII.Summary of background dataCurrent methods to minimize the frequency of SII include local antibiotic therapy (vancomycin powder), betadine irrigation, silver nanoparticles, and passive release from antibiotic-loaded poly(methyl methacrylate) cement beads, all of which have notable weaknesses. A novel implant coating has been developed to address some of these limitations but has not been tested in the environment of a SII.MethodsA biodegradable coating using branched poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(propylene sulfide) (PEG-PPS) polymer was designed to deliver antibiotics. The in vivo performance of this coating was tested in the delivery of either vancomycin or tigecycline in a previously established mouse model of SII. Noninvasive bioluminescence imaging was used to quantify the bacterial burden, and implant sonication was used to determine bacterial colony-forming units (CFUs) from the implant and surrounding bone and soft tissue.ResultsThe PEG-PPS-vancomycin coating significantly lowered the infection burden from postoperative day 3 onwards (P